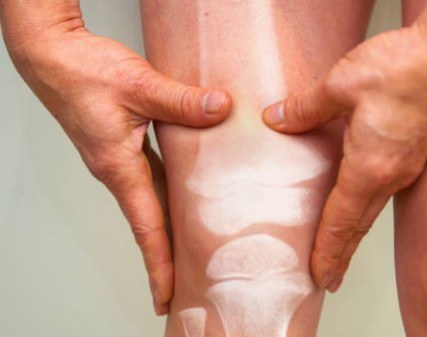
Arthritis is one of the most common chronic health issues affecting senior citizens. It refers to inflammation of the joints, which causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While arthritis can occur at any age, it is especially widespread among older adults, impacting independence and overall quality of life.
🧓 Why Elders Are More Prone to Arthritis
- Age-related wear and tear on joints (osteoarthritis).
- Autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Reduced physical activity leading to joint stiffness.
- Other health factors like obesity, previous injuries, or family history.
🔍 Common Symptoms of Arthritis
- Persistent joint pain and swelling
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after rest
- Limited range of motion
- Tenderness or warmth around joints
- Difficulty performing daily activities like walking, bending, or climbing stairs
✅ How to Mitigate Arthritis in Elders
1. Medical Care
- Early diagnosis is key—consult doctors if pain persists.
- Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, or disease-modifying agents for rheumatoid arthritis.
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and strengthen muscles around joints.
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular low-impact exercise 🏊♀️🚶♂️: Swimming, walking, and yoga reduce stiffness.
- Weight management ⚖️: Maintaining a healthy weight lowers stress on joints.
- Balanced diet 🥗: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (fish, nuts), calcium, and vitamin D support joint and bone health.
3. Home and Self-care
- Heat or cold therapy: Warm compresses ease stiffness; ice packs reduce swelling.
- Assistive devices: Walking aids, supportive shoes, or ergonomic chairs protect joints.
- Joint protection techniques: Avoiding overuse, taking breaks, and using supportive braces.
4. Mental and Emotional Well-being
- Chronic pain may lead to frustration or depression. Support groups, counseling, and staying socially active can improve emotional resilience.
🌟 Conclusion
Arthritis in elders is common but manageable. With timely medical treatment, healthy lifestyle habits, and supportive care, older adults can reduce pain, maintain independence, and enjoy a better quality of life. Families and caregivers play a crucial role in encouraging regular activity, healthy eating, and emotional support.
Arthritis does not have to define aging—proactive management can make all the difference.